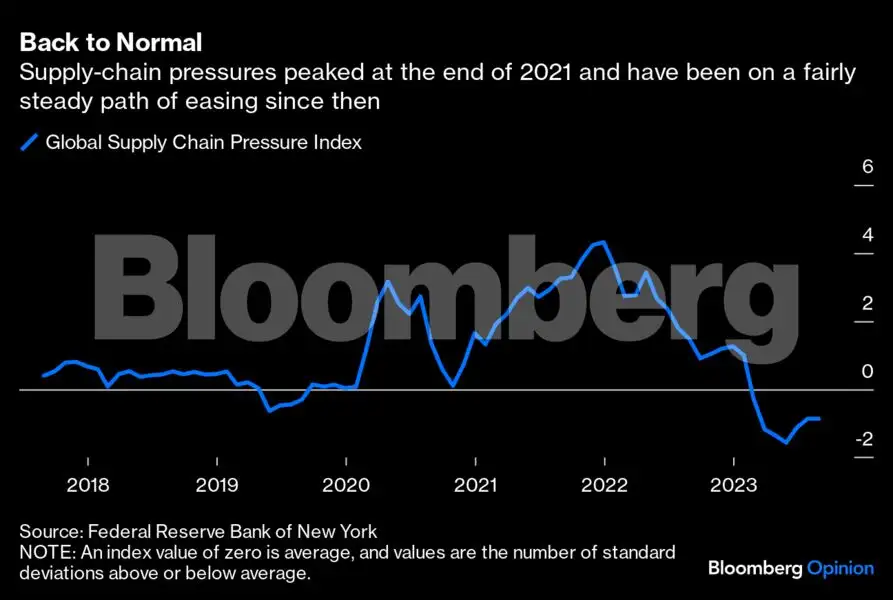
While the term “just-in-time” manufacturing conjures up images of parts whirling through the air and magically landing on a piece of machinery on its way out the door, the concept is really premised on building products according to demand rather than keeping stockpiles of goods on hand in preparation for when they might be needed. It’s a productivity tool but also about quality control and keeping customers happy with on-time deliveries. Nevertheless, during the peak of the pandemic supply-chain crunch, this “just-in-time” coordination of raw materials and parts became a frequent punching bag, with critics arguing manufacturers’ relentless pursuit of efficiency had gone too far and left them vulnerable to disruptions. “Just-in-case” supply chains — whereby companies operate with higher levels of buffer stock to better handle unexpected turmoil — became the mindset of the moment.
Keeping extra inventory around made sense when manufacturing products was akin to playing whack-a-mole with new and frequent problems: semiconductors were in short supply but so were fan blades, plastic buckets and gummy bears; a container ship got stuck in the Suez Canal; and hurricanes, deep freezes and fires shut down factories. But supply chains are now more or less back to normal in most industries outside of aerospace manufacturing, and even there conditions are improving. Freight prices have collapsed as consumers pivot toward spending on services, freeing up capacity and easing the supply-demand imbalance. Events that would have been catastrophic in 2021 — such as a drought in the Panama Canal — are much more navigable in today’s environment.
 iStock
iStockAs such, many companies are suddenly realizing they actually have too much inventory and are now destocking — meaning they’re burning through existing stockpiles of goods rather than placing new orders. What started as pockets of pressure in consumer goods and memory chips has spread to chemicals, home generators, roofing shingles, life sciences, residential air conditioners and heating systems, restaurant-grade kitchen supplies, fire and security products, factory automation technologies and electrical equipment, to name a few. The jump in interest rates has made it more expensive to carry extra inventory. Some companies were also likely overordering to guarantee availability during the supply-chain crunch, and improving wait times mean it’s both possible and necessary to regulate that pace. There’s some debate about whether this destocking trend is a sign of weakening economic demand or merely stabilizing supply chains, but what is clear is that companies are increasingly deciding pandemic-era buffers are no longer necessary.
“With improving lead times, machine builders do not need as many months of products on order and are no longer placing unusually large advance orders,” Rockwell Automation Inc. Chief Executive Officer Blake Moret said on the company’s earnings call in August. Distributors are still sitting on a high level of equipment that’s been committed to a specific customer but is missing some final components. Once that inventory can be cleared and free cash flow freed up, distributors should start placing orders to restock, Moret said in an interview. Still, Rockwell trimmed its outlook for fiscal 2023 orders and its year-end backlog and lowered the high end of its organic growth forecast.
In retail, there are signs that the inventory destocking that has been playing out over the past several quarters is nearing an end. At some point, consumers will have to switch back to buying physical goods again. But companies got burned by a glut of products they couldn’t sell and aren’t eager to overload their shelves again. Trucking company Werner Enterprises Inc. is looking for a return of “normal replenishment” cycles — and that’s an optimistic view. “Mega-retailers remain cautious toward forward inventory stocking and the consumer, while returning to ‘just in time’ inventory strategies and killing the ‘just in case’ promise of the pandemic’s supply chain snarls,” Susquehanna International Group analyst Bascome Majors wrote in an Aug. 31 report when he downgraded the shares of trucking brokers C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc. and RXO Inc. to a negative outlook. Another place where the dismantling of the “just-in-case” inventory mindset is visible is industrial companies’ free cash flow. Manufacturers tracked by Melius Research analyst Scott Davis reported an 84% jump on average in second-quarter free cash flow compared with the period a year earlier when many companies struggled with supply-chain disruptions and excess unfinished or buffer inventory distorted working capital dynamics. Free cash flow conversion among multi-industrial companies still trailed the second-quarter historical norm in the most recent period, according to RBC analyst Deane Dray, but most companies plan to continuing working down elevated working capital balances — meaning they don’t intend to keep extra inventory lying around.
 Bloomberg
BloombergCore & Main Inc., a distributor of pipes, valves and other water equipment, generated $150 million of cash in the most recent quarter by shrinking its inventory. This created “balance sheet capacity to reinvest in the business, pursue strategic M&A and return capital to shareholders,” CEO Steve LeClair said on a call this week to discuss the company’s results. Core & Main raised its outlook for how much operating cash it can extract from its earnings this year because of the accelerated progress the company has made on right-sizing its inventory.General Electric Co. this week hosted a showcase for lean manufacturing, featuring presentations from Ford Motor Co. CEO Jim Farley, Ingersoll Rand Inc.’s Vicente Reynal and Uber Technologies Inc.’s Dara Khosrowshahi, along with famous athletes and chef Wolfgang Puck. Lean manufacturing is a more holistic philosophical umbrella that includes the goals of “just in time” but also seeks continuous improvement in all processes and the elimination of unnecessary waste with an eye toward delivering better safety performance, higher-quality products, more consistent on-time delivery and lower costs — in that order. I attended the event, and I can tell you no one was talking about “just-in-case” supply chains.
Lean manufacturing isn’t by definition anathema to buffers — as long as there’s a reason for them and they create value for the customer. The pandemic illustrated the importance of drilling deeper into the geographical diversity of the supply chain, localizing more of the production process and coordinating more closely with parts and raw materials vendors, but the goal of those efforts is to eliminate unnecessary waste and to reduce slack in the system — not to introduce more of it. Put another way, supply-chain resiliency doesn’t necessarily mean having extra stockpiles of components on hand just for the sake of it. “There’s a whole host of ways to get to a place where you have plenty of inventory, but that’s not translating to high on-time deliveries,” GE CEO Larry Culp told me in an interview last year. “That doesn’t mean we’re not going to have safety stock or buffer, but we want to make sure there’s a deliberate decision taken to do that because of a vendor that may be struggling or anticipated demand spikes we want to be ready for.”
Boeing Update
There was a time around 2019 and 2020 when just about every issue of this newsletter had some kind of bad news update about Boeing Co. On the bright side, there are now longer breaks between the bad news. But the company is still struggling to manufacture and deliver airplanes, which isn’t great because its primary purpose is to manufacture and deliver airplanes. The latest problem involves improperly drilled fastener holes in a critical part of the 737 Max’s structure that helps maintain cabin pressure and was supplied by Spirit AeroSystems Holdings Inc. The defect is proving more complicated to assess and remedy than a separate issue identified earlier this year that affected some of the rear fittings that attach the Max jet’s vertical tail to the body of the plane and also involved Spirit.
The fastener-hole glitch affects three-quarters of the 220 Max planes that Boeing had in inventory at the end of the second quarter, and rooting out the problem requires mechanics to inspect hundreds of holes by X-ray, Chief Financial Officer Brian West said this week in a presentation at the Jefferies industrials conference. Spirit has an additional 39 units in its factory that will require inspection and possibly repairs, and the company doesn’t expect to be finished with that process until the end of November, CEO Tom Gentile said. The work will take longer for Boeing’s inventory of Max jets because those airplanes have largely already been completed and mechanics will have to work around lavatories, kitchen galleys and overhead bins. Boeing now expects Max deliveries this year will be at the low end of its targeted range of 400 to 450 planes as a result of the manufacturing setback. Margins in its commercial aerospace division will be negative in the third quarter, but Boeing is sticking with its forecast for at least $3 billion of free cash flow this year and $10 billion by the middle of the decade.
Gordon made the comments in an interview this week as labor negotiations between the United Auto Workers and General Motors Co., Ford Motor Co. and Jeep-maker Stellantis NV go down to the wire. The union’s membership has voted overwhelmingly to strike if a deal can’t be reached by the time the current contract expires on Sept. 14. UAW President Shawn Fain this week rejected what he said was an “insulting” proposal from GM for a total 16% raise for the top earners in its plants and a 56% boost for newer employees over the life of the contract. The union has asked for a 46% wage increase, the reinstatement of pension plans and benefits for retirees, the elimination of a tiered wage system that delays new employees’ ability to reach the top pay rate, a 32-hour workweek at full 40-hour pay and continued compensation for employees at plants that are closed.
Fain has acknowledged the demands are “audacious,” but they also risk being self-defeating. It’s one thing to ask for workers to get their fair share of elevated profits at the carmakers; this is a logical and justified argument that’s worked for unions in negotiations with Deere & Co., the West Coast ports and United Parcel Service Inc. But Fain has set the union up for a fight over much more than just money. A number of its demands position the union in direct confrontation with the kind of labor force productivity that’s necessary to stay competitive in manufacturing. That’s an uncomfortable place to be when automation technology has improved materially and investments in robotics are on the rise.
 iStock
iStockDeals, Activists and Corporate Governance
WestRock Co. is in talks to merge with Ireland-based packaging rival Smurfit Kappa Group Plc. The combined company would have generated sales of $34 billion and about $5.5 billion in adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization in the 12 months ended June 2023. The packaging business boomed during the pandemic alongside an uptick in demand for e-commerce but has since moderated as consumers shift their spending to services, resulting in a “cardboard box recession.”
 iStock
iStockMerging would allow the companies to cut more than $400 million in annual costs, Smurfit Kappa said in a statement confirming the talks. Conversations are continuing on final terms and there’s no certainty a deal will be struck, but the companies are planning on a primarily stock-based deal, with Smurfit acting as the acquirer. Smurfit is also planning to join an exodus of companies from the UK stock market. The packaging manufacturer expects to cancel its premium listing on the London Stock Exchange, and the combined company would trade on the New York Stock Exchange. That being said, the new Smurfit WestRock would keep its official headquarters address in Ireland, which is attractive to companies because of its favorable tax regime. Elsewhere in packaging news, International Paper Co. CEO Mark Sutton, who has served in that role for almost a decade, has asked theboard to start evaluating candidates to succeed him.
Rockwell Automation Inc.agreed to buy Clearpath Robotics Inc., a company that makes autonomous mobile robots used to transport materials to assembly lines and around the factory floor. The robots will complement the Plex industrial software business that Rockwell acquired in 2021 for $2.2 billion and its independent cart technology. Terms for the Clearpath acquisition weren’t disclosed, but Rockwell said it would use a “portion” of the proceeds from the sale of its stake in industrial software company PTC Inc. Rockwell began unwinding its position in PTC in 2022 and proceeds to date have totaled $1.3 billion, according to Wolfe Research analyst Nigel Coe.
Summit Materials Inc., a cement, concrete and asphalt company, agreed to acquire the US operations of Cementos Argos SA in a cash-and-stock deal valued at $3.2 billion. Argos North America Corp. has four integrated cement plants and about 140 ready-mix plants in the Southeast, mid-Atlantic and Texas and total installed cement grinding capacity of 9.6 million tons a year. Summit says the deal will make it the largest US-based cement producer, positioning the company to better capitalize on growing demand for construction materials in the country as a gush of government funds drives infrastructure upgrades and factory investments. Argos plants are also in sunnier and warmer climates, which reduces the seasonality of Summit’s cement business. The companies are targeting $100 million in annual operational cost savings.
Qantas Airways Ltd. sped up CEO Alan Joyce’s retirement to this week, two months ahead of schedule, amid a public uproar over claims from Australia’s competition watchdog that the carrier last year sold tickets for thousands of flights that it had already canceled. The job of repairing the airline’s crumbling reputation now falls to Vanessa Hudson, a company veteran who was tapped as Joyce’s successor in May. Record profitability at Qantas amid a raft of canceled and delayed flights has fueled debates about whether it’s become too dominant in the Australian market. In a development that can’t be entirely unrelated, the Australian government said it’s evaluating the way takeoff and landing slots are allocated at the main Sydney airport, with any updated rules likely to increase access for upstart airlines such as Rex and Bonza.
Xylem Inc., a $23 billion water technologies company, announced that both its CEO Patrick Decker and its CFO Sandra Rowland are stepping down. Decker will be succeeded by Chief Operating Officer Matthew Pine effective Jan. 1, 2024, while Rowland will be succeeded by William Grogan, who recently stepped down as Idex Corp.’s CFO, starting Oct. 1. Both Decker and Rowland will serve as advisers to Xylem through March 2024 to help with the transition. Xylem only completed the $7.5 billion acquisition of Evoqua Water Technologies Corp. in May, and it’s unusual for companies to change management teams so soon after a large deal. It’s also unusual for both the CEO and CFO to depart at the same time, although not unheard of, especially if the CFO considered herself a successor candidate and feels passed over.
Elsewhere in industrial CEO successions, Illinois Tool Works Inc. announced that longtime leader Scott Santi will step down at the end of the year and be succeeded by Christopher O’Herlihy, a company veteran and the current vice chairman. Santi will transition into a non-executive chairman role. The management transition at ITW shouldn’t surprise investors; Santi had one of the longest tenures among current industrial CEOs and O’Herlihy is well-known to Wall Street, Barclays Plc analyst Julian Mitchell wrote in a note.
Yachts! The Ritz-Carlton Yacht Collection, a provider of luxury travel services that can cost upward of $7,000-a-week per person, is working with Citigroup Inc. to raise as much as $400 million to fund the addition of more ships to its fleet, Bloomberg News reported, citing people with knowledge of the matter. In other fun fundraising news, Amer Sports, the maker of Wilson tennis rackets and Salomon ski boots, has filed for a US initial public offering that could value the company at as much as $10 billion, Bloomberg News reported, citing people familiar with the matter. The company is backed by China’s largest athletic-apparel producer Anta Sports Products Ltd. and also owns brands including Louisville Slugger baseball bats, Arc’teryx outdoor gear and Atomic winter equipment.
Tom Brady is now a Delta Air Lines Inc. employee. The seven-time Super Bowl winner and five-time MVP will be a long-term strategic adviser to the airline and help Delta with training and teamwork tools, marketing and customer engagement. When one thinks of NFL superstars, commercial air travel is generally not the first thing that springs to mind. But Brady says he and his teammates flew Delta “countless times” over the course of his career, “spending hours traveling for some of the most important games of our lives, even celebrating Super Bowl wins on the plane.” The quarterback retired after the 2022 NFL season and has been expanding his portfolio of investments and partnerships, including taking stakes in the British football club Birmingham City and the Las Vegas Aces, a WNBA team. Brady was previously a booster of collapsed cryptocurrency exchange FTX, and January bankruptcy documents indicated he owned more than 1.1 million shares. He is among the celebrities who were sued over their promotion of FTX.








